In an ever-changing world, website performance is more crucial than ever. Website visitors have adopted new behaviors: they have become increasingly demanding and expect pages to load quickly, offering them a fluid experience and not taxing their patience.
This is where Core Web Vitals come in. These metrics are at the heart of the new era of web performance evaluation, not only for user experience, but also for search engine optimization (SEO).
In this article, we'll dive into the world of Core Web Vitals, exploring what they are, why they're essential to website performance and how they impact search engine rankings. We'll also give you the keys to measuring your website's performance, and see how Drupal, which we specialize in, does all it can to optimize these performance metrics.

What are Core Web Vitals ?
These are 3 metrics that measure the performance and user experience of a website, focusing on loading speed (LCP), interactivity (FID) and visual stability (CLS) :
- LCP (largest contentful paint): corresponding to the loading of the "heaviest" content on the page. This could be an image or a video, for example.
- FID (first input delay): corresponding to the user interaction delay.
- CLS (cumulative layout shift): represents the visual stability of the website as the user browses it.
As you can see, the aim is to make the user's journey through your site as easy as possible, and that includes the interface's performance! At WebstanZ, we obviously have a number of elements to which we pay particular attention when creating our sites.

L'impact sur le SEO
SEO is based on 3 major pillars:
- Popularity: basically, the number of quality links pointing to your website.
- Content: long, optimized content that really responds to user expectations and search engine requirements.
- Technical: site performance and code optimization.
Web Core Vitals fall into this third category. All the more reason to pay attention to them, as they can influence your site's visibility on search engines!
(Recently, user experience has been added as the 4th pillar of SEO, but we'll tell you about that in a later article).
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to the process of improving your site's organic traffic and ranking on search engines such as Google, Bing and others.

Two performance measurement tools
There are many free tools available to give you an overview of your site's performance. Let's take a closer look at the 2 key tools offered by Google:
- Google PageSpeed Insights is a tool that not only gives you a quick overview of each of your key web signals, but also provides recommendations for optimizing them. It focuses specifically on optimizing the loading speed of your web pages.
- Google Search console is an interface designed to help website owners monitor their site's presence in Google search results, identify indexing and SEO issues (including web signal concerns) and optimize their visibility in organic search results. The tool focuses on the monitoring, management and presence of your site in search results. It allows you to see how your SEO performance is improving, as well as performance indications for each of your pages.

Analysing results with Google PageSpeed Insights
Once you've created your first report, how do you know if the results are good? For each of the Core Web Vitals, Google provides a metric that allows you to determine whether the value calculated is sufficient or not.
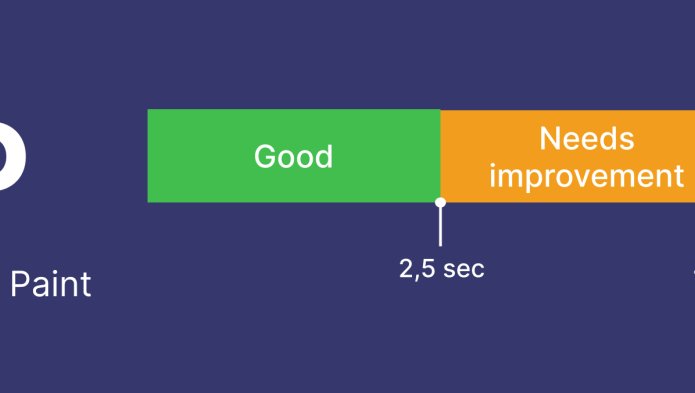
For LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), which corresponds to the perceived loading speed, the metric must be less than 2.5 seconds to be considered satisfactory.
There are several possible reasons for a poor LCP:
- Javascript or CSS code that blocks the rendering of a page, thereby delaying its loading
- Some resources take too long to load (images, videos)
For CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift), which measures visual stability, the loading time must be less than 0.1 seconds to be considered good.
Here are two elements that can cause a poor CLS:
- Images with no predefined dimensions
- Dynamically added content

And finally, FID (First Input Delay), which measures the user's first impression of your site's interactivity and responsiveness. It requires a loading time of less than 100 milliseconds to be satisfactory..
Elements that can cause a poor FID include large javascript files that take a long time to load.

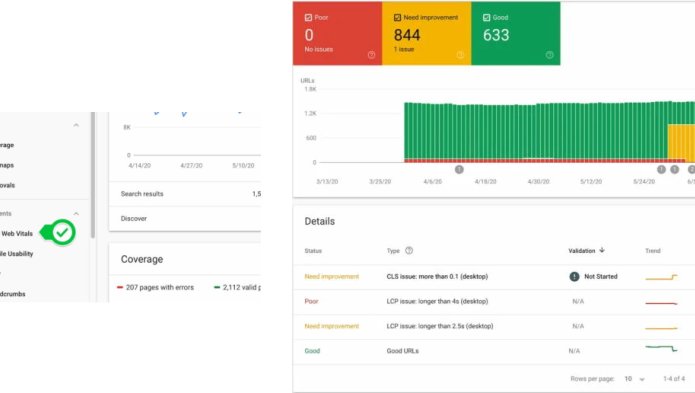
Analysing results with Google Search Console
As the metrics are the same, we're not going to explain it all again :)
Just know that you can also find a report about Core Web Vitals in your Search Console interface. You'll be able to see at a glance which URLs may be causing problems, and how to resolve them.
What about Drupal?
In order to optimise performance as much as possible, Drupal offers users a long list of modules and functions to guarantee optimal loading times.
Image management
Drupal offers a range of image management tools and features to optimise the loading performance of your website. You can automatically resize images to match different predefined styles, compress images to reduce size without compromising quality, and create responsive formats to load images that are suitable for every device.
In addition, Drupal supports modern formats such as WebP, which offers better compression. You can also activate delayed image loading to speed up the initial display of the page, while using the Media module for efficient image management.
By combining all these features to reduce the bandwidth needed to load images, you can meet the requirements of Core Web Vitals, improve the loading performance of your Drupal site, and offer an optimal user experience. All this will also help your site rank higher in search engines!
Reduction of HTTP requests
Drupal offers a number of tools and techniques for reducing HTTP requests on your website, thereby improving loading performance.
You can aggregate CSS and JavaScript files to reduce the number of requests, disable unnecessary files, enable delayed image loading to reduce initial requests, use a CDN to distribute static resources, or optimise third-party resources and take advantage of caching to avoid recurring requests.
By adopting these practices and configuring Drupal properly, you can minimise unnecessary HTTP requests, speed up page loading and deliver a better user experience.

The Drupal cache
Drupal offers a full range of caching tools to optimise website performance. Caching pages, blocks, views and entities allows generated elements to be stored temporarily, reducing the load on the server and speeding up page loading.
Drupal also offers expiration mechanisms to ensure that cached content remains up to date. By combining these features with the appropriate configuration, you can greatly improve the speed of your Drupal website, provide a better user experience and reduce the workload on the database.
Conclusion
Core Web Vitals have become a central element in the evaluation of website performance, playing a crucial role in both user experience and SEO. These metrics, such as loading speed, interactivity and visual stability, reflect how visitors perceive your site. Fast, reliable loading performance improves user engagement, reduces bounce rates and builds trust. What's more, it has become an important ranking factor for search engines.
Drupal, as a powerful and flexible content management system, provides a full range of tools and features to help optimise their Core Web Vitals. From image management to reducing HTTP requests and optimising caching, Drupal offers a multitude of options for improving page load performance. By using these tools and adopting good practices, Drupal websites can offer a fast, fluid and satisfying user experience, while improving their ranking in search results. It is therefore essential to take the Core Web Vitals into account when designing and maintaining a Drupal website, to ensure its competitiveness on the modern web.



